0% found this document useful (0 votes)
177 views10 pagesIslamic Finance Essentials
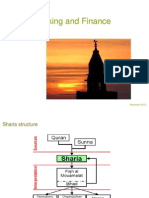
The document discusses the key features and framework of Islamic finance. It notes that Islamic finance is based on Shariah principles from the Quran and hadiths and prohibits interest (riba) and gambling (maisir). The framework includes primary sources like the Quran and Sunnah, as well as secondary sources derived from reasoning like ijma, qiyas and istihsan. Islamic finance also requires real asset backing, risk and profit sharing, and prohibitions against uncertainty. Financial activities must be asset-based and ethically compliant with Shariah values.
Uploaded by
aiman azizCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
177 views10 pagesIslamic Finance Essentials
The document discusses the key features and framework of Islamic finance. It notes that Islamic finance is based on Shariah principles from the Quran and hadiths and prohibits interest (riba) and gambling (maisir). The framework includes primary sources like the Quran and Sunnah, as well as secondary sources derived from reasoning like ijma, qiyas and istihsan. Islamic finance also requires real asset backing, risk and profit sharing, and prohibitions against uncertainty. Financial activities must be asset-based and ethically compliant with Shariah values.
Uploaded by
aiman azizCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10