0% found this document useful (0 votes)
248 views11 pagesReservoir Engineering Midterm Exam
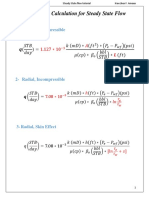
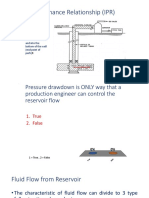
This document is a midterm exam for the course ENGI 8690/9114. It consists of 4 parts worth a total of 100 marks. Part 1 involves unit conversions and physical constants. Part 2 contains 4 numeric problems involving reservoir engineering calculations. Part 3 has 2 problems calculating pressure changes and infinite acting time for a well and reservoir. Part 4 involves using material balance equations to calculate initial oil in place. The exam is to be completed individually over a 2 hour time period.
Uploaded by
Mohammad HaqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
248 views11 pagesReservoir Engineering Midterm Exam
This document is a midterm exam for the course ENGI 8690/9114. It consists of 4 parts worth a total of 100 marks. Part 1 involves unit conversions and physical constants. Part 2 contains 4 numeric problems involving reservoir engineering calculations. Part 3 has 2 problems calculating pressure changes and infinite acting time for a well and reservoir. Part 4 involves using material balance equations to calculate initial oil in place. The exam is to be completed individually over a 2 hour time period.
Uploaded by
Mohammad HaqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11