100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views2 pagesEE8702 - PSOC Syllabus 2017R
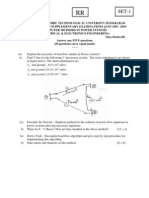
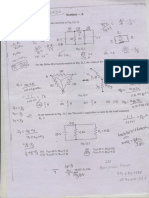
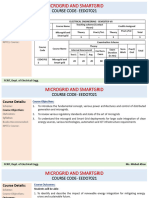
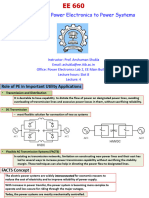
This document outlines the objectives, topics, and outcomes of the course EE8702 Power System Operation and Control. The course aims to impart knowledge about power system operation and control, including real and reactive power interactions and controls, economic operation of power systems, and computer control systems like SCADA. It covers topics like load frequency control, automatic voltage regulation, economic dispatch, and state estimation. The outcomes include understanding day-to-day power system operation and various control actions to meet load variations.
Uploaded by
Raja SekarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views2 pagesEE8702 - PSOC Syllabus 2017R
This document outlines the objectives, topics, and outcomes of the course EE8702 Power System Operation and Control. The course aims to impart knowledge about power system operation and control, including real and reactive power interactions and controls, economic operation of power systems, and computer control systems like SCADA. It covers topics like load frequency control, automatic voltage regulation, economic dispatch, and state estimation. The outcomes include understanding day-to-day power system operation and various control actions to meet load variations.
Uploaded by
Raja SekarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2