0% found this document useful (0 votes)
439 views4 pagesSemester-III Branch-Electrical Engineering & EEE Paper-Electronics Engineering Subject Code: ELE306 Total Hours: 42 Full Marks-100 (80+20)
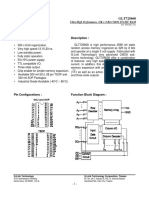
This document outlines the course details for Electronics Engineering. It includes 6 chapters covering topics like semiconductor diodes, rectifiers and filters, bipolar junction transistors, field effect transistors, regulated power supplies, and operational amplifiers. The total course hours are 42 hours. It also includes details of the associated lab course covering practical skills and 10 experiments to be performed.
Uploaded by
RohitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
439 views4 pagesSemester-III Branch-Electrical Engineering & EEE Paper-Electronics Engineering Subject Code: ELE306 Total Hours: 42 Full Marks-100 (80+20)
This document outlines the course details for Electronics Engineering. It includes 6 chapters covering topics like semiconductor diodes, rectifiers and filters, bipolar junction transistors, field effect transistors, regulated power supplies, and operational amplifiers. The total course hours are 42 hours. It also includes details of the associated lab course covering practical skills and 10 experiments to be performed.
Uploaded by
RohitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4