0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views3 pagesLinguistic Elements in Discourse - Summ
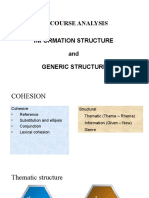
Linguistic elements in discourse include:
1. Cohesion - the connections between elements in a text through words like pronouns.
2. Coherence - the overall fit and unity of ideas in a text.
3. Anaphoric and cataphoric references - words that refer back or forward to other elements mentioned earlier or later in the text.
Lexical cohesion occurs through relationships between words based on their meanings, such as reiteration and collocation. These linguistic elements help create flow and understanding in written and spoken communication.
Uploaded by
Amine BennezzarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views3 pagesLinguistic Elements in Discourse - Summ
Linguistic elements in discourse include:
1. Cohesion - the connections between elements in a text through words like pronouns.
2. Coherence - the overall fit and unity of ideas in a text.
3. Anaphoric and cataphoric references - words that refer back or forward to other elements mentioned earlier or later in the text.
Lexical cohesion occurs through relationships between words based on their meanings, such as reiteration and collocation. These linguistic elements help create flow and understanding in written and spoken communication.
Uploaded by
Amine BennezzarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3