0% found this document useful (0 votes)
331 views100 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollers Guide
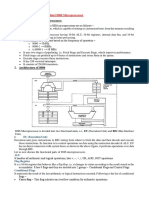
The document discusses microprocessors and microcontrollers. It defines a microprocessor as a central processing unit on a single integrated circuit. It describes the basic components and functions of computers. It also defines microcontrollers as integrated chips that contain a CPU, memory, and I/O ports designed for specific control tasks. Additionally, it outlines characteristics of microprocessors like instruction sets, clock speed, and data bus width.
Uploaded by
JASONCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
331 views100 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollers Guide
The document discusses microprocessors and microcontrollers. It defines a microprocessor as a central processing unit on a single integrated circuit. It describes the basic components and functions of computers. It also defines microcontrollers as integrated chips that contain a CPU, memory, and I/O ports designed for specific control tasks. Additionally, it outlines characteristics of microprocessors like instruction sets, clock speed, and data bus width.
Uploaded by
JASONCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 100