0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views6 pagesDatabase Basics for Beginners
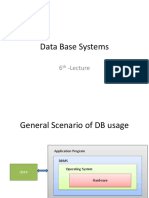
This document discusses the components and languages of databases. It describes users, data, the DBMS software, and database applications as the main components. It also explains the different languages used - data definition language to create and modify database objects, data manipulation language to manage data, and transaction control language to manage transactions. Specific commands like CREATE, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE are discussed with their syntax examples.
Uploaded by
Dan Dexter DimalibotCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views6 pagesDatabase Basics for Beginners
This document discusses the components and languages of databases. It describes users, data, the DBMS software, and database applications as the main components. It also explains the different languages used - data definition language to create and modify database objects, data manipulation language to manage data, and transaction control language to manage transactions. Specific commands like CREATE, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE are discussed with their syntax examples.
Uploaded by
Dan Dexter DimalibotCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6