0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views3 pagesDrug Profile Comparison Between Pitolisant
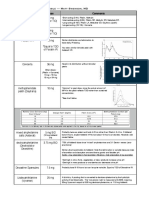
Pitolisant, Armodafinil, and Modafinil are psychostimulant drugs approved to treat excessive daytime sleepiness. Pitolisant is a histamine receptor antagonist, while Armodafinil and Modafinil are indirect dopamine receptor agonists. They have similar dosages and indications to improve wakefulness in adult patients with excessive sleepiness associated with conditions like narcolepsy or sleep apnea. Common adverse effects include headache, nausea, and insomnia. While their mechanisms are not fully understood, they are thought to act on histamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine and orexin systems in the brain.
Uploaded by
akshay dahiweleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views3 pagesDrug Profile Comparison Between Pitolisant
Pitolisant, Armodafinil, and Modafinil are psychostimulant drugs approved to treat excessive daytime sleepiness. Pitolisant is a histamine receptor antagonist, while Armodafinil and Modafinil are indirect dopamine receptor agonists. They have similar dosages and indications to improve wakefulness in adult patients with excessive sleepiness associated with conditions like narcolepsy or sleep apnea. Common adverse effects include headache, nausea, and insomnia. While their mechanisms are not fully understood, they are thought to act on histamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine and orexin systems in the brain.
Uploaded by
akshay dahiweleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3