0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesLoad Testing of Motors: Common Methods, Procedures: Test Can Verify Nameplate Rating
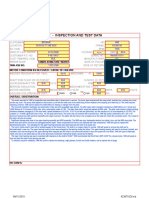
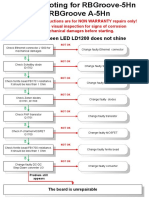
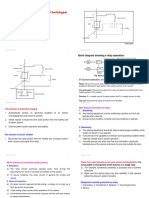
Load testing motors is commonly done using dynamometer testing to verify nameplate performance specifications. Reasons for load testing include detecting faults like an open rotor or incorrect winding design. The load test subjects the motor to its full rated load to measure current, speed, temperature, and slip speed. This helps identify issues like low or high flux and verifies the motor operates as intended according to its nameplate ratings.
Uploaded by
Ali JafferyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesLoad Testing of Motors: Common Methods, Procedures: Test Can Verify Nameplate Rating
Load testing motors is commonly done using dynamometer testing to verify nameplate performance specifications. Reasons for load testing include detecting faults like an open rotor or incorrect winding design. The load test subjects the motor to its full rated load to measure current, speed, temperature, and slip speed. This helps identify issues like low or high flux and verifies the motor operates as intended according to its nameplate ratings.
Uploaded by
Ali JafferyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3