0% found this document useful (0 votes)
224 views4 pagesModule 2 Assignment #1
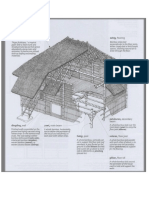
The document defines and describes 21 different parts of a traditional Filipino Bahay Kubo or cube house, providing the local or vernacular term for each part. The main parts include the batalan or back porch, silong or cellar space under the house, bulwagan or main living area, various posts and beams that make up the structural system, components of the pitched roof like the rafters and roofing materials, the sahig or bamboo floor, and features of specific areas like the kitchen and bedrooms. Traditional wall materials are also described.
Uploaded by
JOSEPH SALOSAGCOLCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
224 views4 pagesModule 2 Assignment #1
The document defines and describes 21 different parts of a traditional Filipino Bahay Kubo or cube house, providing the local or vernacular term for each part. The main parts include the batalan or back porch, silong or cellar space under the house, bulwagan or main living area, various posts and beams that make up the structural system, components of the pitched roof like the rafters and roofing materials, the sahig or bamboo floor, and features of specific areas like the kitchen and bedrooms. Traditional wall materials are also described.
Uploaded by
JOSEPH SALOSAGCOLCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4