0% found this document useful (0 votes)
178 views7 pagesFind A Real Root of The Equation F (X) X: Problem
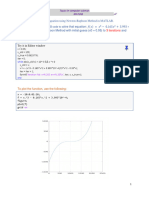
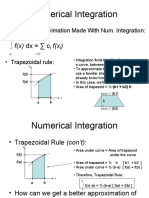
The documents provide MATLAB code to implement numerical integration and interpolation methods, including the trapezoidal rule, Lagrange interpolation, Newton interpolation, linear regression, bisection method, and Newton-Raphson method. The code is demonstrated on examples of integrating functions, finding roots of equations, performing linear regression on data, and interpolating values.
Uploaded by
Md. Faisal ChowdhuryCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
178 views7 pagesFind A Real Root of The Equation F (X) X: Problem
The documents provide MATLAB code to implement numerical integration and interpolation methods, including the trapezoidal rule, Lagrange interpolation, Newton interpolation, linear regression, bisection method, and Newton-Raphson method. The code is demonstrated on examples of integrating functions, finding roots of equations, performing linear regression on data, and interpolating values.
Uploaded by
Md. Faisal ChowdhuryCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7