0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views7 pagesNotes On Project Management
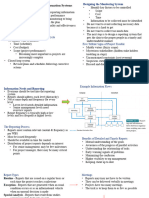
The document discusses key aspects of project management including planning, organizing, coordinating, and controlling projects. It outlines the main tasks of project managers as defining goals and responsibilities, allocating resources, ensuring coordination across teams, and monitoring performance to identify issues and take corrective actions. Additionally, it covers topics such as project monitoring tools, variance analysis, and challenges that can arise in maintaining effective project controls.
Uploaded by
Piyush KumarCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views7 pagesNotes On Project Management
The document discusses key aspects of project management including planning, organizing, coordinating, and controlling projects. It outlines the main tasks of project managers as defining goals and responsibilities, allocating resources, ensuring coordination across teams, and monitoring performance to identify issues and take corrective actions. Additionally, it covers topics such as project monitoring tools, variance analysis, and challenges that can arise in maintaining effective project controls.
Uploaded by
Piyush KumarCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7