100% found this document useful (1 vote)
429 views5 pagesProcess Control
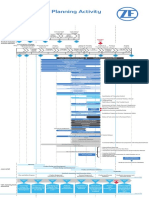
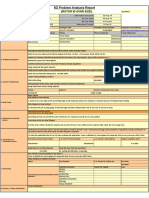
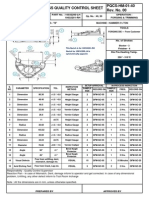
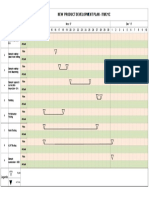
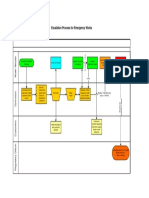
This document outlines an organization's process control procedure. It describes the purpose, scope, responsibilities, and documents related to process control. It also discusses the requirements of relevant ISO and IATF standards. The main sections cover developing process identification, mapping, control, criteria, capability studies, qualification, documentation, and addressing changes and special processes. Product safety measures are also summarized.
Uploaded by
Tuan AnhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
429 views5 pagesProcess Control
This document outlines an organization's process control procedure. It describes the purpose, scope, responsibilities, and documents related to process control. It also discusses the requirements of relevant ISO and IATF standards. The main sections cover developing process identification, mapping, control, criteria, capability studies, qualification, documentation, and addressing changes and special processes. Product safety measures are also summarized.
Uploaded by
Tuan AnhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5