0% found this document useful (0 votes)
567 views2 pagesMemory Read & Write Operations
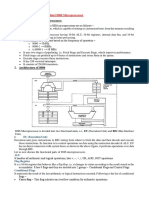
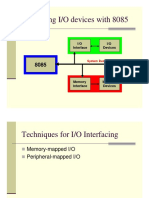
This document discusses read and write operations in memory. It explains that memory stores data in words made up of bits and uses data input/output lines and control lines like Read and Write to transfer data into and out of memory locations indexed by an address bus. It provides an example of calculating memory size in bytes based on the number of address lines and describes the processes of reading and writing data, where reading transfers data from a memory location to the Memory Data Register and writing transfers data from the register to a memory location.
Uploaded by
usman khanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
567 views2 pagesMemory Read & Write Operations
This document discusses read and write operations in memory. It explains that memory stores data in words made up of bits and uses data input/output lines and control lines like Read and Write to transfer data into and out of memory locations indexed by an address bus. It provides an example of calculating memory size in bytes based on the number of address lines and describes the processes of reading and writing data, where reading transfers data from a memory location to the Memory Data Register and writing transfers data from the register to a memory location.
Uploaded by
usman khanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2