0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views10 pagesCorporate Strategy Assignment 2
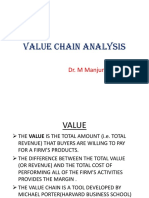
This document provides a SWOT analysis and overview of ITC Limited, an Indian conglomerate. It discusses ITC's diverse business portfolio including FMCG, hotels, packaging, and agribusiness. ITC has strong brands across categories and effective social initiatives that benefit farmers. However, tobacco products remain the largest revenue source. The document also outlines ITC's competitive advantages like unmatched distribution reach and brand building capabilities. Metrics are presented showing ITC's revenue growth across business segments over the last 10 years.
Uploaded by
SRICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
185 views10 pagesCorporate Strategy Assignment 2
This document provides a SWOT analysis and overview of ITC Limited, an Indian conglomerate. It discusses ITC's diverse business portfolio including FMCG, hotels, packaging, and agribusiness. ITC has strong brands across categories and effective social initiatives that benefit farmers. However, tobacco products remain the largest revenue source. The document also outlines ITC's competitive advantages like unmatched distribution reach and brand building capabilities. Metrics are presented showing ITC's revenue growth across business segments over the last 10 years.
Uploaded by
SRICopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10