0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views10 pages3 Spring m3 XML Config Slides
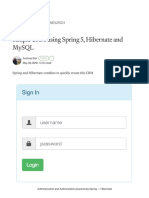
The document discusses XML configuration in Spring. It describes how the applicationContext.xml file acts as a registry and how namespaces aid in configuration and validation. It also explains how beans are defined to represent classes and replace the new keyword, and how setter and constructor injection along with autowiring are used to inject dependencies.
Uploaded by
Mohammed SaadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views10 pages3 Spring m3 XML Config Slides
The document discusses XML configuration in Spring. It describes how the applicationContext.xml file acts as a registry and how namespaces aid in configuration and validation. It also explains how beans are defined to represent classes and replace the new keyword, and how setter and constructor injection along with autowiring are used to inject dependencies.
Uploaded by
Mohammed SaadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10