a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
Implementing Neural Network from
Scratch.
Neural Networks are really powerful algorithms used for classification.
Dataset = Iris_Dataset
Link = http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/datasets/plot_iris_dataset.html
(http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/datasets/plot_iris_dataset.html)
Import required libraries
In [ ]: from sklearn import datasets #for dataset
import numpy as np #for maths
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #for plotting
Get Dataset
In [ ]: iris = datasets.load_iris() #load the dataset
data = iris.data #get features
target = iris.target #get labels
shape = data.shape #shape of data
#convert into numpy array
data = np.array(data).reshape(shape[0],shape[1])
target = np.array(target).reshape(shape[0],1)
#print shape
print("Data Shape = {}".format(data.shape))
print("Target Shape = {}".format(target.shape))
print('Classes : {}'.format(np.unique(target)))
print('Sample data : {} , Target = {}'.format(data[70],target[70]))
Define Parameters and Hyperparameters
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 1 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
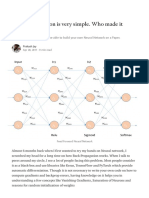
One hidden layer Neural Network.
Input Units = 4
Hidden Units = 8
Output Units = 3
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 2 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
In [ ]: #HYPERPARAMETERS
#num of target labels
num_classes = len(np.unique(target))
#define layer_neurons
input_units = 4 #neurons in input layer
hidden_units = 8 #neurons in hidden layer
output_units = 3 #neurons in output layer
#define hyper-parameters
learning_rate = 0.03
#regularization parameter
beta = 0.00001
#num of iterations
iters = 4001
Dimesions of Parameters
Shape of layer1_weights (Wxh) = (4,8)
Shape of layer1_biasess (Bh) = (8,1)
Shape of layer2_weights (Why) = (8,3)
Shape of layer2_biasess (By) = (3,1)
In [ ]: #PARAMETERS
#initialize parameters i.e weights
def initialize_parameters():
#initial values should have zero mean and 0.1 standard deviation
mean = 0 #mean of parameters
std = 0.03 #standard deviation
layer1_weights = np.random.normal(mean,std,(input_units,hidden_unit
layer1_biases = np.ones((hidden_units,1))
layer2_weights = np.random.normal(mean,std,(hidden_units,output_uni
layer2_biases = np.ones((output_units,1))
parameters = dict()
parameters['layer1_weights'] = layer1_weights
parameters['layer1_biases'] = layer1_biases
parameters['layer2_weights'] = layer2_weights
parameters['layer2_biases'] = layer2_biases
return parameters
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 3 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
Activation Function
Sigmoid
0.5
0
−6 −4 −2 0 2 4 6
In [ ]: #activation function
def sigmoid(X):
return 1/(1+np.exp((-1)*X))
#softmax function for output
def softmax(X):
exp_X = np.exp(X)
exp_X_sum = np.sum(exp_X,axis=1).reshape(-1,1)
exp_X = (exp_X/exp_X_sum)
return exp_X
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 4 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
Define Utility Functions
1. Forward Propagation
---- Logits = matmul(X,Wxh) + Bh
---- A = sigmoid(logits)
---- logits = matmul(A,Why) + By
---- output = softmax(logits)
Store output and A in cache to use it in backward propagation
2. Backward Propagation
---- Error_output = output - train_labels
---- Error_activation = (matmul(error_output,Why.T))(A)(1-A)
---- dWhy = (matmul(A.T,error_output))/m
---- dWxh = (matmul(train_dataset.T,error_activation))/m
m = len(train_dataset)
Store derivatives in derivatives dict
3. Update Parameters
---- Wxh = Wxh - learning_rate(dWxh + betaWxh)
---- Why = Why - learning_rate(dWhy + betaWhy)
4. Calculate Loss and Accuracy
---- Loss = (-1(Y log(prediction)) + (1-Y) (log(1-predictions))) + beta * (sum(Wxh^2) +
sum(Why^2)))/m
---- Accuracy = sum(Y==predictions)/m
In [ ]: #forward propagation
def forward_propagation(train_dataset,parameters):
cache = dict() #to store the intermediate values for bac
m = len(train_dataset) #number of training examples
#get the parameters
layer1_weights = parameters['layer1_weights']
layer1_biases = parameters['layer1_biases']
layer2_weights = parameters['layer2_weights']
layer2_biases = parameters['layer2_biases']
#forward prop
logits = np.matmul(train_dataset,layer1_weights) + layer1_biases
activation1 = np.array(sigmoid(logits)).reshape(m,hidden_units)
activation2 = np.array(np.matmul(activation1,layer2_weights) + laye
output = np.array(softmax(activation2)).reshape(m,num_classes)
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 5 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
#fill in the cache
cache['output'] = output
cache['activation1'] = activation1
return cache,output
#backward propagation
def backward_propagation(train_dataset,train_labels,parameters,cache
derivatives = dict() #to store the derivatives
#get stuff from cache
output = cache['output']
activation1 = cache['activation1']
#get parameters
layer1_weights = parameters['layer1_weights']
layer2_weights = parameters['layer2_weights']
#calculate errors
error_output = output - train_labels
error_activation1 = np.matmul(error_output,layer2_weights.T)
error_activation1 = np.multiply(error_activation1,activation1)
error_activation1 = np.multiply(error_activation1,1-activation1)
#calculate partial derivatives
partial_derivatives2 = np.matmul(activation1.T,error_output)/len
partial_derivatives1 = np.matmul(train_dataset.T,error_activation1
#store the derivatives
derivatives['partial_derivatives1'] = partial_derivatives1
derivatives['partial_derivatives2'] = partial_derivatives2
return derivatives
#update the parameters
def update_parameters(derivatives,parameters):
#get the parameters
layer1_weights = parameters['layer1_weights']
layer2_weights = parameters['layer2_weights']
#get the derivatives
partial_derivatives1 = derivatives['partial_derivatives1']
partial_derivatives2 = derivatives['partial_derivatives2']
#update the derivatives
layer1_weights -= (learning_rate*(partial_derivatives1 + beta*layer
layer2_weights -= (learning_rate*(partial_derivatives2 + beta*layer
#update the dict
parameters['layer1_weights'] = layer1_weights
parameters['layer2_weights'] = layer2_weights
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 6 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
return parameters
#calculate the loss and accuracy
def cal_loss_accuray(train_labels,predictions,parameters):
#get the parameters
layer1_weights = parameters['layer1_weights']
layer2_weights = parameters['layer2_weights']
#cal loss and accuracy
loss = -1*np.sum(np.multiply(np.log(predictions),train_labels) +
accuracy = np.sum(np.argmax(train_labels,axis=1)==np.argmax(predict
accuracy /= len(train_dataset)
return loss,accuracy
Train Function
1. Initialize Parameters
2. Forward Propagation
3. Backward Propagation
4. Calculate Loss and Accuracy
5. Update the parameters
Repeat the steps 2-5 for the given number of iterations
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 7 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
In [ ]: #Implementation of 3 layer Neural Network
#training function
def train(train_dataset,train_labels,iters=2):
#To store loss after every iteration.
J = []
#WEIGHTS
global layer1_weights
global layer1_biases
global layer2_weights
global layer2_biases
#initialize the parameters
parameters = initialize_parameters()
layer1_weights = parameters['layer1_weights']
layer1_biases = parameters['layer1_biases']
layer2_weights = parameters['layer2_weights']
layer2_biases = parameters['layer2_biases']
#to store final predictons after training
final_output = []
for j in range(iters):
#forward propagation
cache,output = forward_propagation(train_dataset,parameters)
#backward propagation
derivatives = backward_propagation(train_dataset,train_labels
#calculate the loss and accuracy
loss,accuracy = cal_loss_accuray(train_labels,output,parameters
#update the parameters
parameters = update_parameters(derivatives,parameters)
#append loss
J.append(loss)
#update final output
final_output = output
#print accuracy and loss
if(j%500==0):
print("Step %d"%j)
print("Loss %f"%loss)
print("Accuracy %f%%"%(accuracy*100))
return J,final_output
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 8 of 9
�a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch - Jupyter Notebook 24/11/2020, 13:10
In [ ]: #shuffle the dataset
z = list(zip(data,target))
np.random.shuffle(z)
data,target = zip(*z)
#make train_dataset and train_labels
train_dataset = np.array(data).reshape(-1,4)
train_labels = np.zeros([train_dataset.shape[0],num_classes])
#one-hot encoding
for i,label in enumerate(target):
train_labels[i,label] = 1
#normalizations
for i in range(input_units):
mean = train_dataset[:,i].mean()
std = train_dataset[:,i].std()
train_dataset[:,i] = (train_dataset[:,i]-mean)/std
In [ ]: #train data
J,final_output = train(train_dataset,train_labels,iters=4001)
Reached an Accuracy of 97%
Plot the loss vs iteration graph
In [ ]: #plot loss graph
plt.plot(list(range(1,len(J))),J[1:])
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Iterations VS Loss')
plt.show()
In [ ]:
http://localhost:8889/notebooks/notebooks/ml-learn/nn/a-simple-neural-network-from-scratch.ipynb Page 9 of 9