0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views2 pagesAdvanced Encryption Techniques
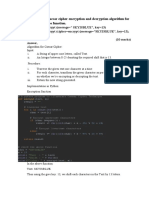
The document describes an encryption algorithm that uses a monoalphabetic substitution cipher with a shift key (SK) to encrypt plaintext in multiple rounds, where each round uses a new substitution table based on the previous round's SK letter. An example encryption is provided where the plaintext "green car has been detected on campus" is encrypted over 4 rounds using different substitution tables based on the SK letters 'e', 'b', and 'd'. The document also proposes implementing automated frequency analysis to decrypt such ciphertexts by analyzing letter frequencies, word lengths, and dictionaries.
Uploaded by
Muhammad SadnoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views2 pagesAdvanced Encryption Techniques
The document describes an encryption algorithm that uses a monoalphabetic substitution cipher with a shift key (SK) to encrypt plaintext in multiple rounds, where each round uses a new substitution table based on the previous round's SK letter. An example encryption is provided where the plaintext "green car has been detected on campus" is encrypted over 4 rounds using different substitution tables based on the SK letters 'e', 'b', and 'd'. The document also proposes implementing automated frequency analysis to decrypt such ciphertexts by analyzing letter frequencies, word lengths, and dictionaries.
Uploaded by
Muhammad SadnoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2