100% found this document useful (1 vote)
221 views2 pagesLevel 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 1
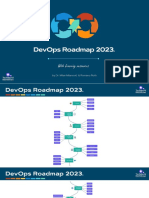
The DevOps maturity model outlines 5 levels of maturity for DevOps practices:
1) Initial - Processes are ad hoc and unpredictable.
2) Defined - Processes are defined but not standardized.
3) Managed - Processes are standardized across projects using modified standard processes.
4) Measured - Process quality and performance are measured for visibility and predictability.
5) Optimized - Continuous process assessment leads to minimal risk and cost achieving objectives.
Uploaded by
satyamulagala1236Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
221 views2 pagesLevel 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 1
The DevOps maturity model outlines 5 levels of maturity for DevOps practices:
1) Initial - Processes are ad hoc and unpredictable.
2) Defined - Processes are defined but not standardized.
3) Managed - Processes are standardized across projects using modified standard processes.
4) Measured - Process quality and performance are measured for visibility and predictability.
5) Optimized - Continuous process assessment leads to minimal risk and cost achieving objectives.
Uploaded by
satyamulagala1236Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2