0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views25 pagesMakalah Expanding Your Knowledge: Mata Kuliah: Writing 1
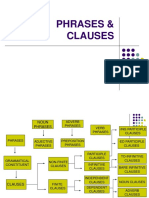
This document provides guidance on expanding writing skills through various grammar concepts. It begins with an introduction and table of contents. It then discusses making words agree, introducing clauses, handling phrases, using adjectives and adverbs, and using prepositions. Examples are provided for each concept. The document aims to help readers improve their writing through practicing correct grammar.
Uploaded by
Karon MeerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views25 pagesMakalah Expanding Your Knowledge: Mata Kuliah: Writing 1
This document provides guidance on expanding writing skills through various grammar concepts. It begins with an introduction and table of contents. It then discusses making words agree, introducing clauses, handling phrases, using adjectives and adverbs, and using prepositions. Examples are provided for each concept. The document aims to help readers improve their writing through practicing correct grammar.
Uploaded by
Karon MeerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 25