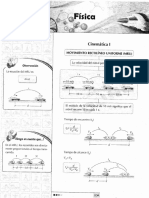
IDEPUNP / CICLO REGULAR SETIEMBRE-DICIEMBRE 2018 1 RAZONAMIENTO MATEMÁTICO
SEMANA Nº 04
TEMA: OPERADORES
Coordinadora: Lic. Rosa Gómez Risco
Responsable: Lic. Ángel Jiménez Chumacero
PROBLEMAS PROPUESTOS 8060
2 Calcular 40 20 .
1. Si a b b 3b .
Calcular: [(2018 (5 (4 5)))] 2 . a) 189/46 b) 189/23 c) 189/64
a) –1 b) –2 c) –3 d) 5 e) 3
d) 189/43 e) 189/34
2. Se define en R: a b (a b) a . Hallar m en:
m (2 3) 3 2 . 9. Se define: ab a b 4
Calcule:
3 1
21 41
a) 0 b) –5 c) 1 d) 5 e) 4
a1 es el elemento inverso de a
# 5 6
a) 4 b) 5 c) 6 d) 7 e) 8
5 6 5
6 5 6 A {1; 0; 1; 2} se define
10. En
3. Si: . Calcular: (56) #(66) .
2 1 0 1
a) 6 b) 5 c) 11 d) 65 e) 56
2 1 0 1 2
1 0 1 2 1
1 1
f x2 2 x4 4 0 1 2 1 0
4. Si x x , calcule f 4 1 2 1 0 1
a) 12 b) 16 c) 18 d) 14 e) 20
x
1 1
1
1 2 0 ( 1)1
Si , entonces x es:
5. Si f ( n) a n b n ; f (1) 2 ; f (2) 3 ; a) 0 b) 1 c) –1
Calcule f (5)
d) –2 e) No se puede determinar
a) 30/7 b) 6/5 c) 29/2 d) 29 e) 18 A= a,b,c,d ,
11. Se define en la siguiente
operación:
a b
6. Si :
a b a 2 b2 a b c d
5 a a b c d
Calcule:
3 b b c d a
c c d a b
a) 1 b) 2 c) 0 d) 8 e) 4
d d a b c
7. Si
m2 m m3; m R
E d a1
1
b1
1
1 Halle:
Calcule:
a)a b) b c) c d)d e) e
1 -1
12. Sabiendo que:
a) -1 b) 0 c) 1 d) 2 e) 2
1 2 3 4
(1 1) (1 2) (1 3) ...(1 n)
mn 1 1 2 3 4
8. Sea m ,
2 2 3 4 5
3 3 4 5 6
4 4 5 6 7
�IDEPUNP / CICLO REGULAR SETIEMBRE-DICIEMBRE 2018 2 RAZONAMIENTO MATEMÁTICO
Halle:
6 7 3 5 :
a) 6 b) 7 c) 8 d) 9 e) 10
a) 15 b) 17 c) 18 d)20 e) 16
13. Si 2x x x 1
1 5 9 13
19. Si
2 3 15 27 39
5 9 21 33 45
x 1 2 x 5 x 3
8 15 27 39 51
11 21 33 45 57
Hallar 12
Calcular: E 98201 .
a) 683 b) 785 c) 814 a) 1 b) 2 c) 0 d) 1 e) 4
d) 795 e) 812 20. Sabiendo que se cumple:
32 20 36
P x / y P x P y 4033 53
14. Si:
P 4 18 25 34
P
Calcule: 2
Calcular x , si 30 x x 30
1
a) 20 b) 30 c) 40 d) 50 e) 60
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 2
x x y y 5 xy 2 y x 1 11 3; 31 5; 51 1; 7 1 7
15. Si ; calcular 21. Si se cumple que .
Además, el elemento neutro toma su máximo valor en
768 3
esta operación cerrada, halla
3 12
M 5* 1 * 3* 7
1 1 1
.
a) -101 b) 121 c) -133 d) 402 e) 261
a) 1 b) 3 c) 5 d) 7 e) – 1
1
x 2
3
16. Si 1 x2 , ¿a qué es igual 22. Calcular el valor de , si dicho operador se
1 x
3x 2 y 3 y
x y x
x define así: .
?
15 15 2 15 15
x2
a) 8 b) 11 c) 9 d) 7 e) 8
b) 1 x
2
a) 2 c) 1 d) 2x e) -1
TAREA DOMICILIARIA
x y x2 y 1
17. Se define xy ;
1. Calcular
E 4 * 4 * 4 *.......
x 1
calcular , Si m * n (2n) 2 3m
a)2 b)3 c) 5 d) 4 e)7
x 4 7
sabiendo que
2. Sean p (a ) a a 3 y q(b) 3b 2 ; determine
4 p(3) 5q (5)
a) 3 b) 5 c) 6 d) 3 e) 5
el valor de q (2 p (2)) .
18. Si
13 3 7 31 33
x x x 1
a) 7 b) 7 c) 6 d) 99 e) 79
x 56
:
Calcular
7
�IDEPUNP / CICLO REGULAR SETIEMBRE-DICIEMBRE 2018 3 RAZONAMIENTO MATEMÁTICO
n 5 , n es positivo
n 2
3. Sea
n 7 , n es negativo
4
Calcule .
a)-1 b)1 c)-3 d) 4 e)2
4. Se define en : a * b ab . Calcule
1
E 31 * 21 * 41 *51
. Obs. a 1 :
elemento inverso de a .
a) 123 b)115 c)165 d)120 e)146
HOJA DE CLAVES
�IDEPUNP / CICLO REGULAR SETIEMBRE-DICIEMBRE 2018 4 RAZONAMIENTO MATEMÁTICO
CICLO: SETIEMBRE – DICIEMBRE 2018
Curso: RAZONAMIENTO MATEMÁTICO
SEMANA: 04
PREGUNTA CLAVE TIEMPO(MIN.) DIFICULTAD
01 B 2 F
02 D 2 F
03 E 2 F
04 D 3 M
05 C 2 F
06 E 4 F
07 C 3 M
08 A 3 F
09 D 3 M
10 C 3 M
11 A 2 F
12 C 3 M
13 D 2 F
14 B 2 F
15 B 2 F
16 C 2 F
17 E 3 M
18 B 3 M
19 D 4 M
20 B 3 M
21 A 3 M
22 E 4 M
TAREA DOMICILIARIA
1 A 3 F
2 B 3 F
3 A 3 F
4 D 3 M