0% found this document useful (0 votes)
280 views5 pagesCHAPTER 3 Notes
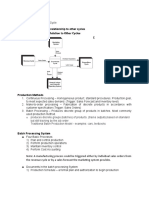
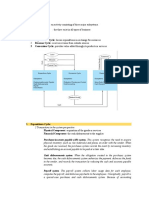
This document contains a 14-question pre-test on concepts related to fraud examination and internal controls. The questions cover elements of the fraud triangle, benefits of internal controls, types of controls such as preventive and detective controls, ethical principles, components of the COSO framework, and examples of specific fraud schemes. Accompanying notes provide explanations or clarifications for some of the questions.
Uploaded by
CHRISTINA HANAVI MILLANCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
280 views5 pagesCHAPTER 3 Notes
This document contains a 14-question pre-test on concepts related to fraud examination and internal controls. The questions cover elements of the fraud triangle, benefits of internal controls, types of controls such as preventive and detective controls, ethical principles, components of the COSO framework, and examples of specific fraud schemes. Accompanying notes provide explanations or clarifications for some of the questions.
Uploaded by
CHRISTINA HANAVI MILLANCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5