100% found this document useful (1 vote)
487 views4 pagesSUD I - Opioid-Related Disorders Cheat Sheet: by Via
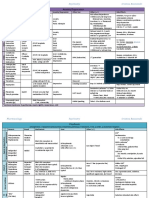
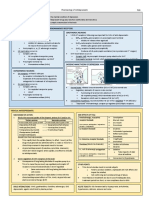
The document provides information on opioid use disorder including terminology, pathophysiology, assessment tools, and treatment options. It discusses natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids. It also summarizes first and second line treatment options such as buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. Key details on buprenorphine formulations and prescribing restrictions are given. Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal and timelines are outlined. Lastly, DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for opioid use disorder are stated.
Uploaded by
Thư PhạmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
487 views4 pagesSUD I - Opioid-Related Disorders Cheat Sheet: by Via
The document provides information on opioid use disorder including terminology, pathophysiology, assessment tools, and treatment options. It discusses natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opioids. It also summarizes first and second line treatment options such as buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone. Key details on buprenorphine formulations and prescribing restrictions are given. Signs and symptoms of opioid withdrawal and timelines are outlined. Lastly, DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for opioid use disorder are stated.
Uploaded by
Thư PhạmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4