0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesUnderstanding Light Sensors
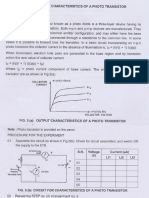
An LDR (light dependent resistor) is a sensor that decreases resistance when exposed to light. It is made of cadmium sulfide, which exhibits photoconductivity by allowing electrons to jump between bands when absorbing photons. This process lowers resistance. LDRs are used in applications like light meters, street lights, and alarms to control circuits based on light intensity.
Uploaded by
Karthik DmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesUnderstanding Light Sensors
An LDR (light dependent resistor) is a sensor that decreases resistance when exposed to light. It is made of cadmium sulfide, which exhibits photoconductivity by allowing electrons to jump between bands when absorbing photons. This process lowers resistance. LDRs are used in applications like light meters, street lights, and alarms to control circuits based on light intensity.
Uploaded by
Karthik DmCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3