0% found this document useful (0 votes)
372 views51 pagesCase Study On AWS
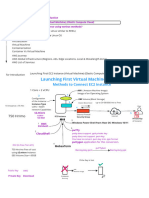
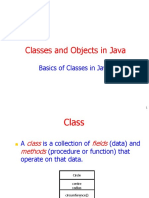
The document provides an overview of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud computing platform. It describes how AWS began in 2006 offering cloud computing infrastructure services and now provides a reliable, scalable, and low-cost cloud platform powering hundreds of thousands of businesses globally. It then outlines the various compute, storage, database, analytics, networking, developer, and other cloud services available in AWS and how users can access and combine them to meet their business needs.
Uploaded by
nitin goswamiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
372 views51 pagesCase Study On AWS
The document provides an overview of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud computing platform. It describes how AWS began in 2006 offering cloud computing infrastructure services and now provides a reliable, scalable, and low-cost cloud platform powering hundreds of thousands of businesses globally. It then outlines the various compute, storage, database, analytics, networking, developer, and other cloud services available in AWS and how users can access and combine them to meet their business needs.
Uploaded by
nitin goswamiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 51