7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
Search …
You are here: Home » MPLS
MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham
Link Course Contents
MPLS
Lesson Contents
1. Configuration Unit 1: Introduction
1.1. Backdoor Link Unit 2: LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
1.2. OSPF Sham Link Unit 3: MPLS VPN
VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding)
OSPF Sham Links are required when you try to use a backdoor link between two CE MPLS L3 VPN Explained
routers in an MPLS VPN PE CE scenario where you use OSPF as the PE-CE routing MPLS L3 VPN Configuration
protocol. This is best explained with an example, take a look at the following topology: MPLS L3 VPN BGP Allow AS in
MPLS L3 VPN BGP AS Override
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE RIP
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE EIGRP
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Default Route
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Global Default
Route
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
VRF Lite Route Leaking
MPLS VPN Extranet Route Leaking
MPLS VPN VRF Export Map
MPLS VPN VRF Import Map
MPLS over FlexVPN
Unit 4: MPLS L2 Encapsulation
Unit 5: IPv6 MPLS
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 1/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
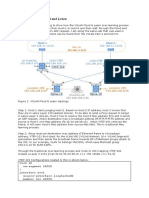
Above we have an MPLS VPN topology where we use OSPF as the PE-CE routing protocol.
Getinterface
CE1 and CE2 each have a loopback Full Access
that to our 731 Cisco
is advertised Lessons
in OSPF Now
area 0. Start
Right now, $1 Trial
the MPLS backbone is the only way for the CE routers to reach each other.
Configurations
Want to take a look for yourself? Here you will find the startup configuration of each
device.
CE1
hostname CE1
ip cef
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no ip address
router ospf 1
network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
end
CE2
hostname CE2
ip cef
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no ip address
router ospf 1
network 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.45.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
end
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 2/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
hostname P
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
!
ip cef
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
mpls ip
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.34.3 255.255.255.0
mpls ip
router ospf 1
network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
end
PE1
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 3/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
hostname PE1
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
!
ip vrf CUSTOMER
rd 1:1
route-target export 1:1
route-target import 1:1
ip cef
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip vrf forwarding CUSTOMER
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
router ospf 2 vrf CUSTOMER
redistribute bgp 234 subnets
network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
router ospf 1
mpls ldp autoconfig
network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
router bgp 234
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 234
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
address-family ipv4
no neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
exit-address-family
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
neighbor 4.4.4.4 send-community extended
exit-address-family
address-family ipv4 vrf CUSTOMER
redistribute ospf 2
exit-address-family
end
PE2
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 4/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
hostname PE2
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
!
ip vrf CUSTOMER
rd 1:1
route-target export 1:1
route-target import 1:1
ip cef
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
ip vrf forwarding CUSTOMER
ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
ip address 192.168.34.4 255.255.255.0
router ospf 2 vrf CUSTOMER
redistribute bgp 234 subnets
network 192.168.45.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
router ospf 1
mpls ldp autoconfig
network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 192.168.34.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
router bgp 234
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 234
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
address-family ipv4
no neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
exit-address-family
address-family vpnv4
neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community extended
exit-address-family
address-family ipv4 vrf CUSTOMER
redistribute ospf 2
exit-address-family
end
Let’s take a look at the routing tables of our CE routers:
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 5/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
CE1#show ip route ospf
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
5.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 5.5.5.5 [110/3] via 192.168.12.2, 00:09:22, GigabitEthernet0/1
O IA 192.168.45.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.12.2, 00:09:22,
GigabitEthernet0/1
CE2#show ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O IA 1.1.1.1 [110/3] via 192.168.45.4, 00:09:36, GigabitEthernet0/1
O IA 192.168.12.0/24 [110/2] via 192.168.45.4, 00:09:36,
GigabitEthernet0/1
The CE routers see each other’s loopback interfaces as an inter-area route through the
OSPF “super backbone”. Let’s try a traceroute just to be sure that our CE routers can
reach each other:
CE1#traceroute 5.5.5.5 source 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 5.5.5.5
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.12.2 5 msec 7 msec 5 msec
2 192.168.23.3 [MPLS: Labels 17/19 Exp 0] 9 msec 11 msec 9 msec
3 192.168.45.4 [MPLS: Label 19 Exp 0] 9 msec 12 msec 10 msec
4 192.168.45.5 9 msec 10 msec *
1. Configuration
1.1. Backdoor Link
Time to mess things up. Let’s add a backdoor link between CE1 and CE2. This could be a
backup link that you want to use in case the MPLS VPN provider has issues:
Let’s enable OSPF on this interface and advertise it in area 0:
CE1(config)#router ospf 1
CE1(config-router)#network 192.168.15.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
CE2(config)#router ospf 1
CE2(config-router)#network 192.168.15.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
The total cost through the MPLS VPN network is 4. Let’s increase the metric for our
backdoor link to 100:
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 6/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
CE1 & CE2
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
(config)#interface GigabitEthernet 0/2
(config-if)#ip ospf cost 100
Let’s see which interface our CE routers now want to use:
CE1#show ip route ospf
5.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 5.5.5.5 [110/101] via 192.168.15.5, 00:00:22,
GigabitEthernet0/2
O 192.168.45.0/24 [110/101] via 192.168.15.5, 00:00:22,
GigabitEthernet0/2
CE2#show ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 1.1.1.1 [110/101] via 192.168.15.1, 00:00:27,
GigabitEthernet0/2
O 192.168.12.0/24 [110/101] via 192.168.15.1, 00:00:27,
GigabitEthernet0/2
Despite the higher cost, CE1 and CE2 prefer the backdoor link. This is because OSPF
always prefers intra-area routes over inter-area routes.
CE1#traceroute 5.5.5.5 source 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 5.5.5.5
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.15.5 7 msec 4 msec *
1.2. OSPF Sham Link
The only way to fix this is to advertise the routes that are learned through the MPLS VPN
network as intra-area routes. We can do this with the OSPF sham link. The sham link is a
logical link, similar to a virtual link. It allows you to create a point-to-point connection
between the two PE routers. The PE routers are then able to flood LSAs across the MPLS
VPN backbone. You don’t have to configure anything on the CE routers.
The sham link is established between two IP addresses that have to be in the VRF of the
customer. To achieve this, we will create a new loopback interface on each PE router
which is advertised in BGP:
PE1: 22.22.22.22/32
PE2: 44.44.44.44/32
Let’s start with PE1:
PE1(config)#interface loopback 1
PE1(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding CUSTOMER
PE1(config-if)#ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255
Let’s advertise this IP address in BGP:
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 7/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
We're Sorry, Full Content Access is for Members Only...
If you like to keep on reading, Become a Member Now! Here is why:
Learn any CCNA, CCNP and CCIE R&S Topic. Explained As Simple As Possible.
Try for Just $1. The Best Dollar You’ve Ever Spent on Your Cisco Career!
Full Access to our 731 Lessons. More Lessons Added Every Week!
Content created by Rene Molenaar (CCIE #41726)
Give Membership a try - it's just $1 ►
491 Sign Ups in the last 30 days
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed!
You may cancel your monthly membership at any time.
No Questions Asked!
« Previous Lesson
MPLS L3 VPN PE-CE OSPF
Global Default Route
Next Lesson
VRF Lite Route Leaking »
Tags: IP Routing
Forum Replies
ReneMolenaar
That’s correct. MPLS VPN PE-CE with OSPF as the routing protocol between PE/CE.
ReneMolenaar
Hello Minh,
Redistributed routes in OSPF on a CE router is no problem. You only need a sham link when you have a backdoor link in between your CE routers.
By default, OSPF external routes don’t get redistributed into BGP but you can change that. Here’s a quick example:
CE1(config)#interface Loopback 1
CE1(config-if)#ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255
CE1(config)#ip access-list standard CE1_L0
CE1(config-std-nacl)#permit host 11.11.11.11
CE1(config)#route-map CE1_L1 permit 10
CE1(config-route-map)#match ip address CE1_L1
CE1(config)#router ospf 1
CE1(
... Continue reading in our forum
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 8/9
�7/26/2021 MPLS Layer 3 VPN PE-CE OSPF Sham Link
Get Full Access to our 731 Cisco Lessons Now Start $1 Trial
dongquangminh
Thank you, Rene.
Rgds,
Minh
lagapides
Hello @pradyumnayadavgla
It seems that you posted this in a private message. I will quote it here, and respond to it so that all of our readers can benefit.
Hi Rene,
Q1- Sham link can only be used for CE-PE OSPF not with other IGP like EIGRP and RIP?
Q2- can it is possible to use sham link when we are using OSPF for CE-PE connectivity
and other IGP using for providing reachability b/w IBGP neighbors or vice versa?
Q3- Did not understand concept of MPLS VPN backbone mean which link will act as
MPLS VPN backbone and if sham link is the MPLS VPN backbone link me
... Continue reading in our forum
lagapides
Hello Pradyumna
Whenever you require a sham link for OSPF, this is due to the fact that a customer has obtained a backup link between the customer sites, most often
with the goal of providing redundancy. This means that there will be two possible paths that data can take between two particular customer sites, one via
the MPLS network, and the other via the backup link.
Usually, an MPLS network will be the primary method of interconnecting sites, due to the fact that it is typically a high performance network, and because
customers will often have more than two
... Continue reading in our forum
3 more replies! Ask a question or join the discussion by visiting our Community Forum
© 2013 - 2021 NetworkLessons.com Disclaimer Privacy Policy Support About
https://networklessons.com/mpls/mpls-layer-3-vpn-pe-ce-ospf-sham-link 9/9