0% found this document useful (0 votes)
170 views16 pagesSpeaking Definition
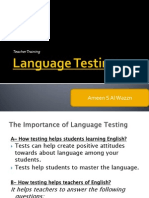
The document discusses theories related to assessing speaking ability. It defines speaking as a productive skill that can be observed through tests, but notes tests are influenced by listening ability. Speaking requires linguistic and sociolinguistic competence. When assessing speaking, factors like accent, grammar, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension should be evaluated. Scores are given on a scale of 0+ to 4+ to indicate proficiency levels. There are three main types of speaking assessments: imitative, intensive, and responsive.
Uploaded by
Javed KhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
170 views16 pagesSpeaking Definition
The document discusses theories related to assessing speaking ability. It defines speaking as a productive skill that can be observed through tests, but notes tests are influenced by listening ability. Speaking requires linguistic and sociolinguistic competence. When assessing speaking, factors like accent, grammar, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension should be evaluated. Scores are given on a scale of 0+ to 4+ to indicate proficiency levels. There are three main types of speaking assessments: imitative, intensive, and responsive.
Uploaded by
Javed KhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16