0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesPLC Interview Questions and Answers
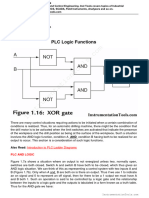
This document provides information about programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in the form of interview questions and answers. It begins with 20 multiple choice questions that test basic knowledge of PLC components, functions, and applications. This is followed by 6 questions that are answered in paragraph form, covering topics like the main components of a PLC, advantages over hardwired relay systems, common programming languages, the role of the central processing unit, the scan process, and differences between PLCs and general purpose computers. The document concludes by listing 8 key advantages of PLCs over traditional hardwired control systems.
Uploaded by
Jêmš NavikCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesPLC Interview Questions and Answers
This document provides information about programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in the form of interview questions and answers. It begins with 20 multiple choice questions that test basic knowledge of PLC components, functions, and applications. This is followed by 6 questions that are answered in paragraph form, covering topics like the main components of a PLC, advantages over hardwired relay systems, common programming languages, the role of the central processing unit, the scan process, and differences between PLCs and general purpose computers. The document concludes by listing 8 key advantages of PLCs over traditional hardwired control systems.
Uploaded by
Jêmš NavikCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6