0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views8 pagesOOP-Lab Week5 With Solution - Tagged
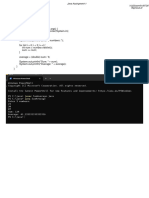
This document contains an instructor lab manual for an object oriented programming course. It includes 6 programming exercises with solutions in Java. The exercises cover topics like getting user input, comparing numbers, solving quadratic equations, and identifying vowels/consonants. The document provides the code solutions to each exercise on the corresponding page.
Uploaded by
Sara MohCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views8 pagesOOP-Lab Week5 With Solution - Tagged
This document contains an instructor lab manual for an object oriented programming course. It includes 6 programming exercises with solutions in Java. The exercises cover topics like getting user input, comparing numbers, solving quadratic equations, and identifying vowels/consonants. The document provides the code solutions to each exercise on the corresponding page.
Uploaded by
Sara MohCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8