GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
System Software - Operating Systems
What is system software?
System software is software which allows a computer to run and to be maintained.
“Operating System” software and “Utility Software” are the two main types of system
software.
The Operating System
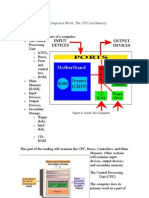
The operating system is the most important piece of software on any computer. Without it,
no programs will run. This is because an operating system is responsible for controlling /
communicating with the computer hardware. It provides a platform on which games,
browsers, music players etc, can all work.
If you were to run an everyday program (e.g. a word processor),
without an operating system, nothing would be displayed on the
screen, nothing could be sent to the printer, nothing could be typed.
This is because application software, does not know how to TALK to
hardware devices. However, the operating system does. The
operating system can also talk to the application that is running. So
when you print a document, the application talks to the OS, which in
turn talks to the printer.
The operating system sits between the user’s applications and the
hardware. It enables applications to use the hardware resources.
The Kernel
The kernel is the heart of the operating system and is responsible
for looking after “the most low-level hardware operations”. It is the
kernel that applications make use of when they want to operate
the computer’s hardware.
The 5 Major Roles of the Operating System
Ultimately, the operating system provides 5 major roles:
• Memory Management
• Peripheral Management
• Multi-Tasking
• Security
• User Interface
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
1
� GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
Memory Management
The OS manages the RAM. When you load an application, the OS will
copy the application to the RAM. In addition, the OS will ensure that
each program that loads has its own space on the RAM. This stops other
programs reading and writing to the memory area for another
application. It is also responsible for managing virtual memory.
Peripheral Management
Peripherals are devices that are attached to a computer such as a
printer or speakers. The operating system controls these devices and
gives programs access to them. When you print a document, the
program doesn’t know how to talk to the printer, it doesn’t even know if
one is installed. Instead it passes this data to the operating system
which in turn passes it to the printer. The same happens when you
save a file. The program passes this information to the operating
system and the operating system is what saves files onto the hard disk.
The User Interface
The word interface means ‘coming together’. In computers, an
interface enables a user to interact with a computer. Operating
Systems provide users with an interface so that they can interact with
the computer. Operating systems will usually offer one of three major
types of interface:
• Graphical User Interface (GUI)
• Menu Driven Interface
• Command Line Interface
Graphical User Interfaces
Uses windows, icons, menus and pointers (WIMP) to control the
computer. Only been around since the mid 80s. Windows and
Apple Mac OSx are examples of this kind of interface.
Menu Driven Interface
Uses menus to control the computer. These were very popular on
early mobile phones and are seen in all high streets on cash
machines and also on many MP3 players. Only offer limited
functions (ie. if it is not on the menu then you can’t do it!)
Command Line Interface
Used to be the only way to interact with a computer (pre-80s)
and is still used today by ‘Linux users’ and other professionals with
technical knowledge. With this kind of interface ‘written
commands’ control computers.
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
2
� GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
Multi-Tasking
As we know, a CPU’s core works one process at a time. An
operating system enables multi-tasking by managing the CPU’s
processes so that several programs can run at once. On old
computers, a CPU would focus on the processes of one program.
On a multi-tasking operating system, many programs can run at the
same time. The operating system enables this to happen by either
allowing processes to take it in turn, or getting the shortest job
done first. Because CPU’s are so quick now-a-days, it appears to
be simultaneous and allows many programs to be used at once.
Security
Often computers will be used by several users. Operating systems manage these users
and ensure that a user’s data is only seen by them and not by others. In this way an OS
provides security to users. They give users ‘usernames’ and
‘passwords’ so that data is kept secure. They also give different
users different permissions. This means that one user may be
given permission to install new programs whereas others
cannot. In this way, an operating system can ensure that a
computer system is not open to abuse from any user.
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
3
� GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
Questions (The question zone you choose must either match your target grade or be higher!)
Question Zone 1-3
1. Define the term ‘System Software’. [2]
2. “The CPU sits between the user’s applications and the hardware”. What is meant by
this statement? [3]
3. Briefly describe the 5 major roles of an ‘Operating System’.[5]
Question Zone 4-6
1. Briefly describe the 5 major roles of an ‘Operating System’.[5]
2. Explain how the OS manages memory. [4]
3. Explain how the OS enables multi-tasking. [4]
Question Zone 7-9
1. Explain how the OS enables multi-tasking. [4]
2. Explain the role of the ‘Kernel’ in an ‘Operating System’. [2]
3. Discuss the need for the 3 major types of interface. [6]
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
4
� GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
Checklist: Keywords / Key Terms:
Operating System (OS): Software, which manages the hardware and software
Date and title, clearly presented resources of a computer system and provides an interface for the user.
Spelling & grammar checked Kernel: The heart of the operating system, responsible for looking after “the
Question numbers in the margin most low-level hardware operations”.
Multi-Tasking: The ability of an OS to supply the CPU with instructions from
Handwriting neat & legible multiple programs in particular orders to create the illusion that a computer is
Punctuation / Capital letters processing multiple programs simultaneously.
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
5
� GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________
• State/Identify/Give/Name: Simply label a diagram, fill out a table or write a few words
• Describe: Describing is ‘saying what you see’ (E.G.: A computer will have a CPU, Primary and Secondary storage etc)
• Explain: Explaining is ‘saying WHY/HOW something is like that’. (E.G.: A computer will have a CPU so that it can process
all of the data the computer needs to perform a range of tasks. Primary and Secondary storage is needed because…)
• Discuss: Discussing is ‘looking at two sides of an issue, weighing up the two views and giving a conclusion’. Often these
require a mini essay answer. (E.G.: New technology could be seen as being bad for the environment because…, but
on the other hand, new technology has led to… In conclusion I believe that…)
• Describe/Explain/Discuss using examples: Finally, if you are asked to give examples in any of these types of questions –
YOU MUST GIVE EXAMPLES!
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
6
� GCSE Computer Science (9-1)
Stick answer sheet here
Reflections: Score: / Grade:
On / Above / Below
Percentage: % Progress:
What Went Well?: My answers effectively incorporated technical terminology.
I demonstrated a good level of understanding. My responses were well structured / organised.
I responded to the command words effectively. My revision strategy was effective as I showed depth of
My answers were detailed / were written in depth. understanding in my answers.
My work was well presented / legible. My answers contained enough points / examples / explanations
to achieve the marks available.
Even Better If…: I must incorporate key terminology into my answers.
I must better organise my answers to improve its clarity.
My answers need to be more accurate.
I need to improve my revision strategy as I did not
I must respond correctly to the command words.
demonstrate a depth of understanding in my answers.
My answers need more detail / greater depth.
My answers didn’t contain enough points / examples /
I must take greater care over my work / write neatly. explanations to achieve the marks available.
Further thoughts:
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Computer Science UK Membership Site Licence: Do not share outside your centre.
7