0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views26 pagesSystem Dynamics and Control: Unggul Wasiwitono
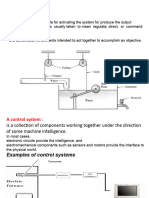
This document introduces the topic of system dynamics and control. It defines a control system as consisting of subsystems and processes assembled to obtain a desired output given a specified input. Historically, feedback control began with early efforts to harness nature, and includes developments in liquid level control, steam pressure control, speed control, and stability criteria. By the late 20th century, control systems became ubiquitous in applications ranging from household products to transportation and manufacturing, underpinning modern society. Improved control systems are important for issues like product quality, efficiency, and environmental protection in manufacturing industries.
Uploaded by
Heru TheerteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views26 pagesSystem Dynamics and Control: Unggul Wasiwitono
This document introduces the topic of system dynamics and control. It defines a control system as consisting of subsystems and processes assembled to obtain a desired output given a specified input. Historically, feedback control began with early efforts to harness nature, and includes developments in liquid level control, steam pressure control, speed control, and stability criteria. By the late 20th century, control systems became ubiquitous in applications ranging from household products to transportation and manufacturing, underpinning modern society. Improved control systems are important for issues like product quality, efficiency, and environmental protection in manufacturing industries.
Uploaded by
Heru TheerteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26