0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views16 pagesJava Basics Batch30
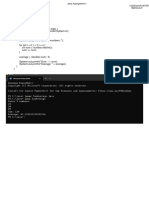
The document contains code snippets demonstrating various Java programming concepts such as:
1. Declaring and initializing variables of different primitive data types and performing arithmetic operations on them.
2. Printing out the minimum and maximum values that can be stored in byte, short, int and long primitive data types.
3. Examples of logical operators, conditional statements like if-else, switch case, ternary operator.
4. Iteration statements like for, while, do-while loops and examples of iterating over ranges.
5. Examples of unary, bitwise operators, string operations.
6. Methods to check if a year is a leap year, find maximum of 3 numbers, count digits
Uploaded by
manikanta tarunCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views16 pagesJava Basics Batch30
The document contains code snippets demonstrating various Java programming concepts such as:
1. Declaring and initializing variables of different primitive data types and performing arithmetic operations on them.
2. Printing out the minimum and maximum values that can be stored in byte, short, int and long primitive data types.
3. Examples of logical operators, conditional statements like if-else, switch case, ternary operator.
4. Iteration statements like for, while, do-while loops and examples of iterating over ranges.
5. Examples of unary, bitwise operators, string operations.
6. Methods to check if a year is a leap year, find maximum of 3 numbers, count digits
Uploaded by
manikanta tarunCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16