100% found this document useful (1 vote)
286 views18 pagesTourism Information Technology: 3 Edition
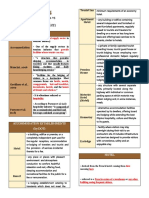
The document summarizes key concepts about the digital tourism landscape from Chapter 2 of the textbook "Tourism Information Technology". It describes the digital tourism ecosystem as consisting of a technological environment, roles of entities/communities, and functions like inspiration, transaction, and experience. It also outlines major waves of IT adoption historically and important developments in internet/technology, ecommerce/social media, and the tourism/hospitality industry from 1995 to the present.
Uploaded by
Kurniawan Gilpuy GilangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
286 views18 pagesTourism Information Technology: 3 Edition
The document summarizes key concepts about the digital tourism landscape from Chapter 2 of the textbook "Tourism Information Technology". It describes the digital tourism ecosystem as consisting of a technological environment, roles of entities/communities, and functions like inspiration, transaction, and experience. It also outlines major waves of IT adoption historically and important developments in internet/technology, ecommerce/social media, and the tourism/hospitality industry from 1995 to the present.
Uploaded by
Kurniawan Gilpuy GilangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18