0% found this document useful (0 votes)
558 views5 pagesQuestion Bank Answer: UNIT 4: Company Formation
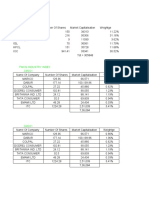
The document provides answers to questions about company formation. It defines the mandatory clauses of a Memorandum of Association, including the name, registered office, object, liability, and capital clauses. It explains the different types of shares (equity and preference) and debentures (registered/bearer, secured/unsecured, redeemable/non-redeemable, convertible/non-convertible). It also discusses the name, registered office, object, capital, and liability clauses in more detail and explains how to alter a Memorandum of Association.
Uploaded by
ameyk89Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
558 views5 pagesQuestion Bank Answer: UNIT 4: Company Formation
The document provides answers to questions about company formation. It defines the mandatory clauses of a Memorandum of Association, including the name, registered office, object, liability, and capital clauses. It explains the different types of shares (equity and preference) and debentures (registered/bearer, secured/unsecured, redeemable/non-redeemable, convertible/non-convertible). It also discusses the name, registered office, object, capital, and liability clauses in more detail and explains how to alter a Memorandum of Association.
Uploaded by
ameyk89Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5