0% found this document useful (0 votes)
107 views4 pagesGATE CS Syllabus
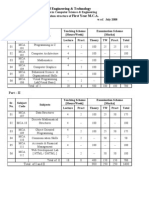
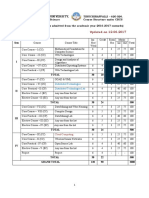
The document provides an overview of the syllabus for a Computer Science and Information Technology program. It covers topics such as engineering mathematics, digital logic, computer organization and architecture, programming and data structures, algorithms, theory of computation, compiler design, operating systems, databases, information systems, computer networks, and web technologies. It also provides references for further study, recommending specific books and suggesting time frames for covering each topic.
Uploaded by
dennisfrancisCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
107 views4 pagesGATE CS Syllabus
The document provides an overview of the syllabus for a Computer Science and Information Technology program. It covers topics such as engineering mathematics, digital logic, computer organization and architecture, programming and data structures, algorithms, theory of computation, compiler design, operating systems, databases, information systems, computer networks, and web technologies. It also provides references for further study, recommending specific books and suggesting time frames for covering each topic.
Uploaded by
dennisfrancisCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4