0% found this document useful (0 votes)
646 views9 pagesFlynn's Classification
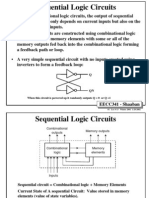
This document discusses Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies computer architectures based on how instructions operate on data. It describes the four categories: Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instructions Multiple Data (MIMD), and Multiple Instructions Single Data (MISD). SISD refers to traditional sequential computing, SIMD involves one instruction operating on multiple data simultaneously, MIMD uses multiple instruction streams on multiple data streams, and MISD is not commonly used and involves multiple instructions operating on a single data stream.
Uploaded by
Geeta MeenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
646 views9 pagesFlynn's Classification
This document discusses Flynn's taxonomy, which classifies computer architectures based on how instructions operate on data. It describes the four categories: Single Instruction Single Data (SISD), Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD), Multiple Instructions Multiple Data (MIMD), and Multiple Instructions Single Data (MISD). SISD refers to traditional sequential computing, SIMD involves one instruction operating on multiple data simultaneously, MIMD uses multiple instruction streams on multiple data streams, and MISD is not commonly used and involves multiple instructions operating on a single data stream.
Uploaded by
Geeta MeenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9