0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views20 pagesAccelerated Data Migration Using LSMW 1.6: R/3 System
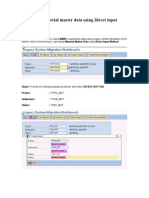
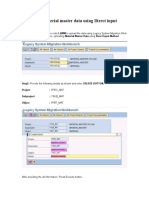
This document provides instructions for using LSMW 1.6 to migrate material master data from an existing system to an SAP R/3 system. It involves defining the migration object, source structures and fields, object dependencies and field mappings. The migration object is defined as material master and will use transaction code RMDATIND for direct input. Source structures for material basic data and consumption data are defined and fields are copied from a reference project. Structure relationships and field mappings are then created to map the source and target systems for loading the data.
Uploaded by
wilmes ferreiraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views20 pagesAccelerated Data Migration Using LSMW 1.6: R/3 System
This document provides instructions for using LSMW 1.6 to migrate material master data from an existing system to an SAP R/3 system. It involves defining the migration object, source structures and fields, object dependencies and field mappings. The migration object is defined as material master and will use transaction code RMDATIND for direct input. Source structures for material basic data and consumption data are defined and fields are copied from a reference project. Structure relationships and field mappings are then created to map the source and target systems for loading the data.
Uploaded by
wilmes ferreiraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20