0% found this document useful (0 votes)
167 views9 pagesCCNA Routing Protocols Assessment
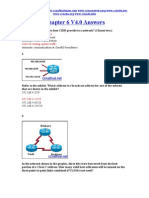
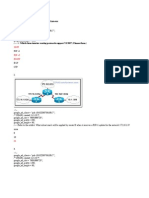
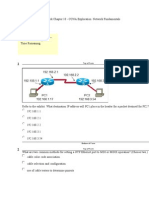
This document contains a series of multiple choice questions about networking concepts like routing, VLSM, CIDR, and subnetting. The questions cover topics such as determining the range of networks summarized by a route, identifying valid host IP addresses based on subnet masks, calculating wasted addresses when applying VLSM, and benefits of protocols like CIDR.
Uploaded by
jkzhCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
167 views9 pagesCCNA Routing Protocols Assessment
This document contains a series of multiple choice questions about networking concepts like routing, VLSM, CIDR, and subnetting. The questions cover topics such as determining the range of networks summarized by a route, identifying valid host IP addresses based on subnet masks, calculating wasted addresses when applying VLSM, and benefits of protocols like CIDR.
Uploaded by
jkzhCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9