0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views6 pagesWhat Is Amazon EC2
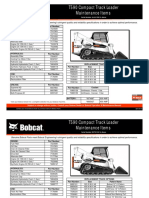
Amazon EC2 provides scalable computing capacity in the AWS cloud using virtual servers. It allows users to launch as many or few virtual servers as needed, configure security and networking, and manage storage. EC2's features include virtual computing environments known as instances, templates for instances known as AMIs, configurable computing capacities known as instance types, secure login information using key pairs, temporary and persistent storage options, multiple physical locations for resources known as regions and availability zones, security groups for firewall rules, static IP addresses known as elastic IPs, metadata tags, and private virtual networks known as VPCs.
Uploaded by
Rocky ArunnCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views6 pagesWhat Is Amazon EC2
Amazon EC2 provides scalable computing capacity in the AWS cloud using virtual servers. It allows users to launch as many or few virtual servers as needed, configure security and networking, and manage storage. EC2's features include virtual computing environments known as instances, templates for instances known as AMIs, configurable computing capacities known as instance types, secure login information using key pairs, temporary and persistent storage options, multiple physical locations for resources known as regions and availability zones, security groups for firewall rules, static IP addresses known as elastic IPs, metadata tags, and private virtual networks known as VPCs.
Uploaded by
Rocky ArunnCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6