0% found this document useful (0 votes)
141 views2 pagesOTV Cheatsheet V1.00 PDF
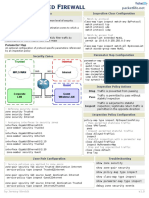
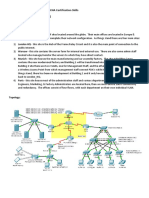
The document summarizes the encapsulation process used in OTV 2.5. It describes how an original Ethernet frame is encapsulated with outer MAC and IP headers to transmit across an overlay network. Key information included are the fields in the overlay encapsulation, such as the overlay ID, instance ID, and reserved bits. Terminology related to OTV components and operations are also defined.
Uploaded by
Oliver Asturiano AbdaláCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
141 views2 pagesOTV Cheatsheet V1.00 PDF
The document summarizes the encapsulation process used in OTV 2.5. It describes how an original Ethernet frame is encapsulated with outer MAC and IP headers to transmit across an overlay network. Key information included are the fields in the overlay encapsulation, such as the overlay ID, instance ID, and reserved bits. Terminology related to OTV components and operations are also defined.
Uploaded by
Oliver Asturiano AbdaláCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2