0% found this document useful (0 votes)
399 views6 pagesClass 10 Notes Controlcoordination
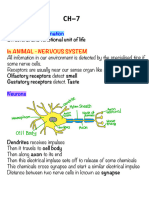
This document contains a summary of class 10 science notes on control and coordination. It discusses the main parts of the brain like cerebrum and cerebellum. It describes the functions of sensory neurons, cranium, vertebral column, and motor neurons. Reflex arc and an example of photoreception in the eye are explained. Plant movements and hormones are also summarized, including the roles of auxin and gibberellins. Key endocrine glands and their functions are identified.
Uploaded by
Vijayasimha rao RavooriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
399 views6 pagesClass 10 Notes Controlcoordination
This document contains a summary of class 10 science notes on control and coordination. It discusses the main parts of the brain like cerebrum and cerebellum. It describes the functions of sensory neurons, cranium, vertebral column, and motor neurons. Reflex arc and an example of photoreception in the eye are explained. Plant movements and hormones are also summarized, including the roles of auxin and gibberellins. Key endocrine glands and their functions are identified.
Uploaded by
Vijayasimha rao RavooriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6