0% found this document useful (0 votes)
859 views7 pagesFourier Series Solved Problems
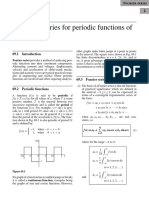
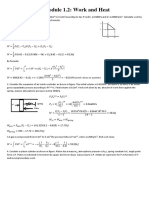
This document provides solutions to problem 5.11 from Solution Set X for the course 18.075-Fall 2004. The problem asks to expand four functions in Fourier series over different intervals:
1) f(x) = a + bx from 0 to P is expanded as a constant plus sine terms.
2) f(x) = 1 for x > 0 and 0 for x < 0 from -1 to 1 is expanded as a constant plus sine terms.
3) f(x) = sin(x) from 0 to pi is expanded as a constant plus cosine and sine terms.
4) f(x) = x from 1 to 2 is expanded with integrals to find the
Uploaded by
MeenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
859 views7 pagesFourier Series Solved Problems
This document provides solutions to problem 5.11 from Solution Set X for the course 18.075-Fall 2004. The problem asks to expand four functions in Fourier series over different intervals:
1) f(x) = a + bx from 0 to P is expanded as a constant plus sine terms.
2) f(x) = 1 for x > 0 and 0 for x < 0 from -1 to 1 is expanded as a constant plus sine terms.
3) f(x) = sin(x) from 0 to pi is expanded as a constant plus cosine and sine terms.
4) f(x) = x from 1 to 2 is expanded with integrals to find the
Uploaded by
MeenaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7