0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesEye Structure and Functions Guide
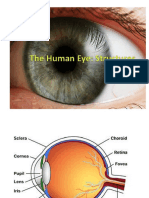
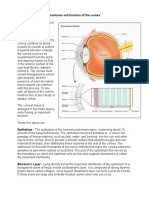
The eye contains several layers that work together to allow sight. The outermost sclerotic layer protects the eyeball, while the cornea refracts light. Inside are the choroid, which absorbs stray light and supplies blood, and the retina containing rod and cone cells that contain the sensory cells for sight. Between the lens and cornea is the aqueous humor that transmits light and supports the eyeball, and the lens focuses images onto the retina.
Uploaded by
Hajara FawaisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesEye Structure and Functions Guide
The eye contains several layers that work together to allow sight. The outermost sclerotic layer protects the eyeball, while the cornea refracts light. Inside are the choroid, which absorbs stray light and supplies blood, and the retina containing rod and cone cells that contain the sensory cells for sight. Between the lens and cornea is the aqueous humor that transmits light and supports the eyeball, and the lens focuses images onto the retina.
Uploaded by
Hajara FawaisCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2