0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views27 pagesComponent of Computer
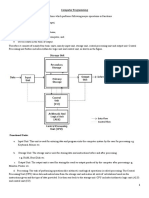
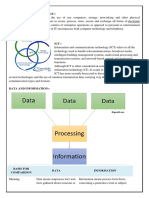
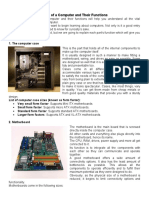
All computers follow the same basic logical structure and perform five basic operations: taking input, storing data, processing data, outputting information, and controlling workflow. The central processing unit (CPU) is considered the brain of the computer and performs all data processing operations. The CPU has three main components - the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for arithmetic and logic operations, the memory unit for storing data and instructions, and the control unit for directing operations. Common computer input devices include the keyboard, mouse, joystick, light pen, trackball, scanner, and digital tablet.
Uploaded by
Huleshwar Kumar SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views27 pagesComponent of Computer
All computers follow the same basic logical structure and perform five basic operations: taking input, storing data, processing data, outputting information, and controlling workflow. The central processing unit (CPU) is considered the brain of the computer and performs all data processing operations. The CPU has three main components - the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for arithmetic and logic operations, the memory unit for storing data and instructions, and the control unit for directing operations. Common computer input devices include the keyboard, mouse, joystick, light pen, trackball, scanner, and digital tablet.
Uploaded by
Huleshwar Kumar SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27