0% found this document useful (0 votes)
502 views9 pagesWhat Is Normalization in DBMS
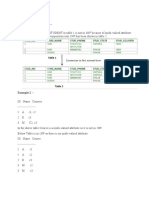
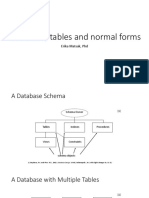
Normalization is a database design technique that reduces data redundancy and eliminates undesirable characteristics like data anomalies. It involves dividing larger tables into smaller tables and linking them using relationships. The document discusses various normal forms including 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, and higher normal forms. It provides examples to illustrate how a sample database can be normalized by removing anomalies and reaching higher normal forms through table decomposition. The goal of normalization is to structure data logically and optimize database design.
Uploaded by
SiuMing ChanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
502 views9 pagesWhat Is Normalization in DBMS
Normalization is a database design technique that reduces data redundancy and eliminates undesirable characteristics like data anomalies. It involves dividing larger tables into smaller tables and linking them using relationships. The document discusses various normal forms including 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, and higher normal forms. It provides examples to illustrate how a sample database can be normalized by removing anomalies and reaching higher normal forms through table decomposition. The goal of normalization is to structure data logically and optimize database design.
Uploaded by
SiuMing ChanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9