0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views12 pagesGenerations of Computer
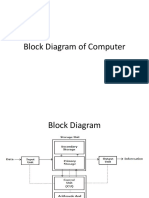
The document discusses the five generations of computers from the 1940s to present. First generation computers used vacuum tubes and were enormous in size. Second generation saw the introduction of transistors, making computers smaller. Third generation used integrated circuits on silicon chips. Fourth generation had microprocessors that located all components on a single chip. Fifth generation computers are still being developed and are focused on artificial intelligence.
Uploaded by
Ajay KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views12 pagesGenerations of Computer
The document discusses the five generations of computers from the 1940s to present. First generation computers used vacuum tubes and were enormous in size. Second generation saw the introduction of transistors, making computers smaller. Third generation used integrated circuits on silicon chips. Fourth generation had microprocessors that located all components on a single chip. Fifth generation computers are still being developed and are focused on artificial intelligence.
Uploaded by
Ajay KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12