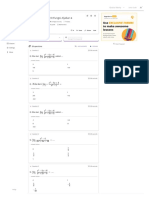
ASSESSMENT NURSING PLANNING IMPLEMENTATION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Subjective data: Deficient fluid Short term goals: Independent: Short term goals:
n/a volume related to
excessive fluid loss Within 8 hours of - Monitor intake and - Provides After 8 hours of interventions and
Objective data: as evidenced by interventions and output (I&O). Note information about constant nurse-client interaction,
- weak, and pale diarrhea and constant nurse-client number, character, and overall fluid patient was able to:
looking vomiting interaction, patient amount of stools. balance, renal
will be able to: Estimate insensible function, and bowel - maintain fluid and electrolyte
- eyes were sunken fluid losses like disease control, as balance
and with observable - maintain fluid and diaphoresis. Measure well as guidelines
discomfort electrolyte balance urine specific gravity for fluid - prevent onset of infection
and replacement.
- frequent watery - prevent onset of observe for oliguria Long term goal:
stools infection
After 3 days of rendering nursing
- facial mask of pain Long term goal: - Observe for - Indicates excessive intervention the patient was able to
excessively dry skin fluid loss or re-establish and maintain normal
- sunken eyes, Within 3 days of and mucous resultant pattern of bowel functioning.
shrivelled skin, with rendering nursing membranes, decreased dehydration.
dark urine intervention the skin turgor, slowed
patient will be able to capillary refill.
- guarding and re-establish and
tenderness noted in the maintain normal
left iliac fossa and pattern of bowel - Weigh daily - Indicator of overall
hypogastrium functioning. fluid and nutritional
status
- Vita Signs taken as
folows: -Encourage the patient -Increase fluid
BP: 90/50 to take at least 1500ml intake replenishes
P: 122bpm to 2000ml of fluid plus the fluid deficit in
R: 28cpm 200ml for each loose the body and
stool prevent dehydration.
-Encourage patient to -A fibre diet helps to
eat fibre containing absorb the fluid and
diets such as cereal, thicken the stool.
grain, and Metamucil.
This study source was downloaded by 100000792113510 from CourseHero.com on 10-26-2022 23:25:59 GMT -05:00
� -To prevent
-Patient teaching should diarrheal illnesses
emphasize principles of due to infection
safe food preparation,
with special attention to
meat preparation and
cooking.
-Monitor laboratory -To monitor
values: electrolyte / patient’s progress
blood during
hospitalization
-Monitor the input and -To evaluate for
output of fluids every 8 responses to
hours. pharmacologic
interventions
Collaborative:
-Provide and monitor -Replacement of
IV fluids as indicated fluid loss
(collaboration).
-Administer antiemetics -Used to control
( e.g. dimenhydrinate) nausea and
as vomiting in acute
indicated attack.
-Administer -Antimicrobial
medications as therapy for cholera
indicated. Give an oral is an adjunct to fluid
antibiotic to the patient therapy
with severe dehydration
as prescribed
This study source was downloaded by 100000792113510 from CourseHero.com on 10-26-2022 23:25:59 GMT -05:00
� This study source was downloaded by 100000792113510 from CourseHero.com on 10-26-2022 23:25:59 GMT -05:00
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)