0% found this document useful (0 votes)
197 views15 pagesFinal Output
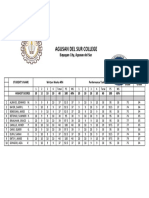
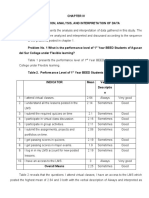
This document contains a 25 question multiple choice exam on topics related to education, learning, motivation, and curriculum development. Some key points covered include Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, Jean Piaget's stages of intellectual development, characteristics of attention deficiency hyperactivity disorder, principles of teaching students with diverse needs, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, goal-setting theory, and metacognition. The exam also asks questions about curriculum stakeholders, curriculum models, and advantages of educational television.
Uploaded by
melody longakitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
197 views15 pagesFinal Output
This document contains a 25 question multiple choice exam on topics related to education, learning, motivation, and curriculum development. Some key points covered include Howard Gardner's theory of multiple intelligences, Jean Piaget's stages of intellectual development, characteristics of attention deficiency hyperactivity disorder, principles of teaching students with diverse needs, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, goal-setting theory, and metacognition. The exam also asks questions about curriculum stakeholders, curriculum models, and advantages of educational television.
Uploaded by
melody longakitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15