0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views18 pages7 - C Knowledge Representation
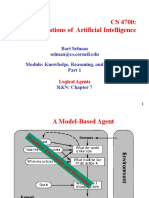
This document discusses knowledge representation in artificial intelligence. It describes how knowledge-based agents use a knowledge base to store information about the world and perform reasoning. The knowledge base contains sentences in a knowledge representation language that represent facts and relationships. Operations like adding new information and querying information can involve inference to derive new knowledge. Different methods for representing knowledge are discussed, including logic, semantic networks, frames and rules. The characteristics of good knowledge representation systems, like inferential adequacy, are also covered. An example application called the Wumpus World is described to illustrate how a knowledge-based agent can operate in a simulated environment.
Uploaded by
Pratik RajCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views18 pages7 - C Knowledge Representation
This document discusses knowledge representation in artificial intelligence. It describes how knowledge-based agents use a knowledge base to store information about the world and perform reasoning. The knowledge base contains sentences in a knowledge representation language that represent facts and relationships. Operations like adding new information and querying information can involve inference to derive new knowledge. Different methods for representing knowledge are discussed, including logic, semantic networks, frames and rules. The characteristics of good knowledge representation systems, like inferential adequacy, are also covered. An example application called the Wumpus World is described to illustrate how a knowledge-based agent can operate in a simulated environment.
Uploaded by
Pratik RajCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18