0% found this document useful (0 votes)
146 views6 pagesGenogram: Family Mapping Tool
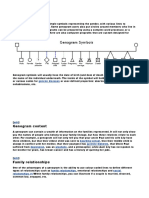
A genogram is a graphic representation of a family tree that displays relationships and patterns of functioning within a family. It was developed in the 1970s as a therapeutic tool and allows therapists to quickly identify patterns in a client's family history that may influence their present situation. A genogram maps out at least three generations and uses symbols and lines to represent family members and relationships. Common information included are family structure, relationships, illnesses, and emotional bonds. The goal is to provide insight into how family dynamics and past events may relate to a client's current problems or concerns.
Uploaded by
Syed Wajahat AliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
146 views6 pagesGenogram: Family Mapping Tool
A genogram is a graphic representation of a family tree that displays relationships and patterns of functioning within a family. It was developed in the 1970s as a therapeutic tool and allows therapists to quickly identify patterns in a client's family history that may influence their present situation. A genogram maps out at least three generations and uses symbols and lines to represent family members and relationships. Common information included are family structure, relationships, illnesses, and emotional bonds. The goal is to provide insight into how family dynamics and past events may relate to a client's current problems or concerns.
Uploaded by
Syed Wajahat AliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6